





When you’re starting a construction project, designing an industrial structure, or even tackling a DIY home improvement task, one of the biggest decisions you’ll face is choosing the right type of metal material. Sounds simple, right? But here’s the catch—expanded metal, wire mesh, and sheet metal may look similar at first glance, yet each offers unique strengths, weaknesses, and applications.
Think of it like picking the right shoes. You wouldn’t wear hiking boots to a beach party, and you wouldn’t wear flip-flops to climb a mountain. Metals work the same way—the wrong choice can cost you money, durability, and efficiency in the long run.
In this guide, we’ll break down the differences between expanded metal vs. wire mesh vs. sheet metal, explain their manufacturing processes, highlight common uses, and give you a practical metal selection guide so you can confidently pick the best fit for your project.
By the end, you’ll know:
What makes expanded metal sheets so versatile.
Why wire mesh applications are critical in industries from construction to agriculture.
How different sheet metal types hold up under various conditions.
And most importantly—which metal is right for you.
So, let’s dive in and clear up the confusion once and for all.
If you’ve ever walked across a sturdy metal walkway with a diamond-shaped pattern or noticed protective grilles around heavy machinery, chances are you’ve already encountered expanded metal. But what exactly is it?
Expanded metal is created by taking a solid sheet of metal and cutting it into a specific pattern before stretching it. This process transforms a plain sheet into a mesh-like surface with diamond or hexagonal openings—without wasting material. Unlike wire mesh, which is woven or welded from separate strands, expanded metal is made from a single continuous piece of sheet metal, making it stronger and more durable.
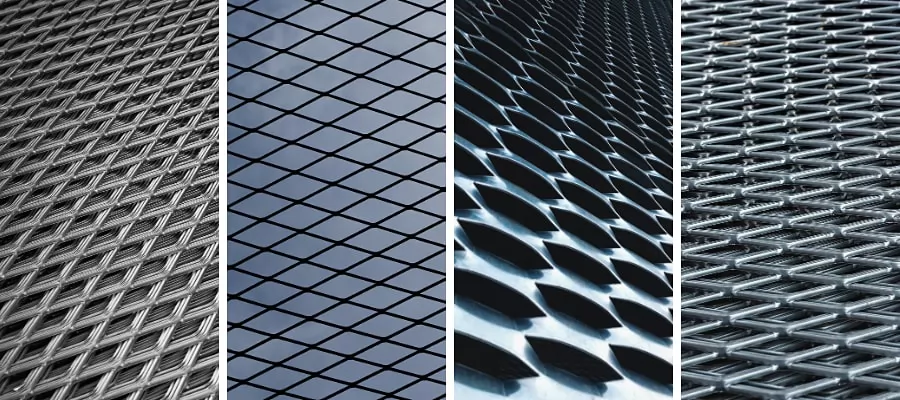
Because of its strength, ventilation capability, and slip-resistant texture, expanded metal finds its way into countless industries. Some popular expanded metal uses include:
Construction: walkways, catwalks, stair treads, and fencing.
Security: machine guards, window security panels, and protective barriers.
Architecture & Design: decorative facades, sunscreens, and interior design accents.
Industrial Applications: filtration systems, ventilation covers, and support grids.
Like every material, expanded metal has its strengths and limitations. Let’s break it down:
Advantages:
Stronger than wire mesh because it’s made from one solid sheet.
Lightweight yet durable.
Excellent airflow, drainage, and light passage.
Slip-resistant surface for flooring and safety applications.
Cost-effective with minimal waste during production.
Disadvantages:
Edges can be sharp if not finished properly.
Not as flexible or easily customized as wire mesh.
May not provide the same smooth aesthetic as sheet metal for decorative applications.
In short, expanded metal sheets are perfect when you need durability, ventilation, and strength combined. But before deciding, it’s important to see how it stacks up against wire mesh—our next contender.
If expanded metal is the “stretched version” of sheet metal, then wire mesh is the “woven fabric” of the metal world. Instead of cutting and stretching a sheet, wire mesh is made by weaving or welding together separate wires into a grid-like structure.
You’ve probably seen it everywhere—from fences and window screens to concrete reinforcement in construction. Its versatility is what makes wire mesh one of the most widely used metal materials today.
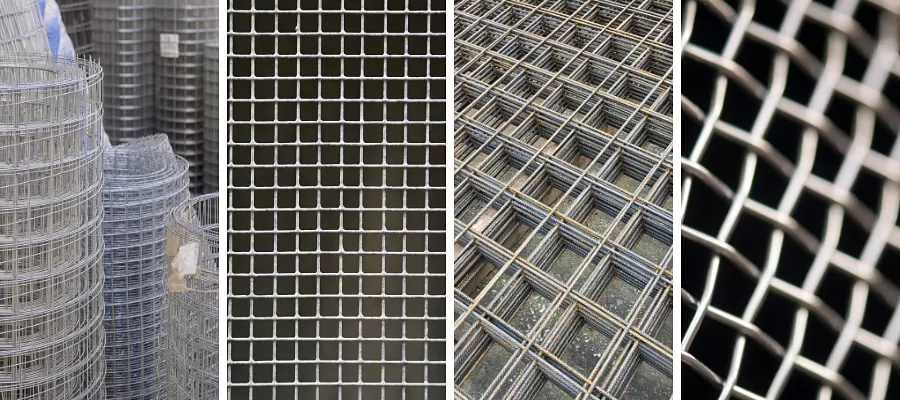
Wire mesh is known for its adaptability, and that’s why it shows up in countless projects:
Construction: reinforcing concrete, fencing, and plaster support.
Industrial: filtration, sieving materials, and machine guards.
Agriculture: animal cages, poultry enclosures, and crop protection.
Residential: window screens, garden fencing, and security barriers.
In other words, wire mesh is like the “Swiss army knife” of metal materials—simple, affordable, and reliable.
Advantages:
Lightweight and easy to install.
Available in many sizes, gauges, and patterns.
Flexible (woven mesh) or rigid (welded mesh) depending on needs.
Cost-effective, especially for fencing and reinforcement.
Excellent for wire mesh applications like filtration and screening.
Disadvantages:
Weaker than expanded metal since it’s made of individual wires.
Can loosen or break under heavy loads.
Not as durable in high-impact or security-heavy environments.
Requires coating (galvanized, PVC, or stainless steel) to resist rust in outdoor use.
To sum it up, wire mesh shines when flexibility, cost-efficiency, and lightweight structure are priorities. But what if you need something completely solid, with no openings at all? That’s when sheet metal enters the picture.
Unlike expanded metal and wire mesh, which have visible openings, sheet metal is a continuous, solid piece of metal that can be cut, bent, or fabricated into almost any shape. It’s essentially the blank canvas of the metal world, offering endless possibilities for construction, manufacturing, and design.
Sheet metal is produced by rolling metal into thin, flat sheets. The thickness can vary, from extremely thin foils used in packaging to heavy-duty plates used in industrial structures. This versatility is what makes sheet metal a cornerstone material across countless industries.
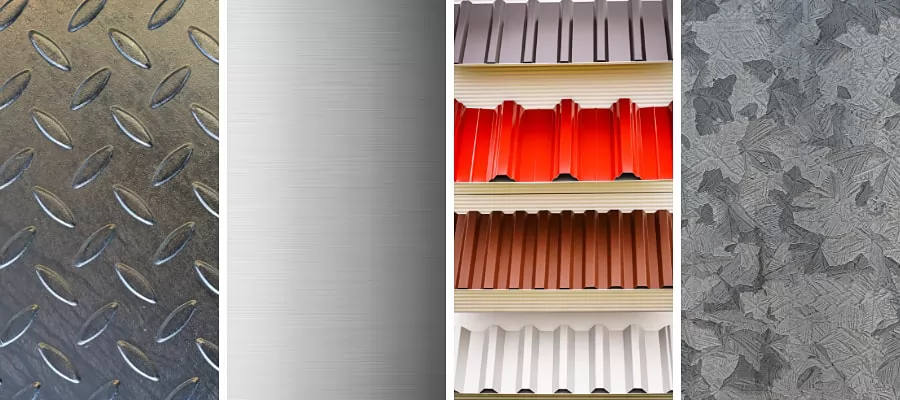

The magic of sheet metal lies in its ability to be shaped and transformed. Common fabrication techniques include:
Cutting: Using shears, lasers, or plasma cutters to size the sheet.
Bending: Creating angles and curves for structural components.
Stamping and Punching: Forming detailed shapes or holes in the sheet.
Welding and Assembly: Joining sheet metal pieces into a final product.
From car body panels to HVAC ducts, sheet metal fabrication is极 at the heart of modern manufacturing.
Advantages:
Extremely versatile and customizable.
Offers a smooth, solid surface for both functional and decorative purposes.
Available in many thicknesses and materials.
Strong, durable, and long-lasting when maintained properly.
Disadvantages:
Can be heavier than expanded metal or wire mesh.
More expensive depending on material type (stainless steel and copper are costly).
Requires additional fabrication to achieve ventilation or decorative patterns.
Without proper coatings, certain types can rust or corrode over time.
In short, sheet metal is your best option when you need a solid, durable surface with maximum flexibility in shaping and design. But now comes the big question—how do these three compare side by side? That’s where a direct comparison makes things clear.
Now that we’ve explored each material individually, let’s put them side by side. While expanded metal, wire mesh, and sheet metal can all be used in construction, manufacturing, and design, their strengths, weaknesses, and ideal applications differ significantly.
Think of it like comparing different vehicles: a pickup truck, a motorbike, and a sedan all get you from point A to B, but the choice depends on whether you’re hauling cargo, commuting daily, or cruising on weekends. The same logic applies here—choosing the right metal depends on your project’s requirements.
| Feature / Material | Expanded Metal | Wire Mesh | Sheet Metal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structure | Cut and stretched from a single sheet | Woven or welded wires | Solid flat sheet |
| Strength & Durability | Strong, rigid, slip-resistant | Moderate (varies by type) | Very strong, especially in thicker gauges |
| Weight | Lightweight but sturdy | Lightest option overall | Heavier (depends on thickness) |
| Ventilation & Visibility | Excellent (openings allow airflow and drainage) | Good (grid-like openings) | None (solid surface) |
| Cost | Moderate (efficient production, minimal waste) | Generally low-cost | Varies widely (steel is affordable, stainless/copper more expensive) |
| Flexibility | Limited flexibility | 极High flexibility (woven types) | Very high (can be cut, bent, shaped) |
| Common Uses | Walkways, fencing, safety grilles | Fencing, filtration, cages, concrete reinforcement | Roofing, automotive parts, appliances, architectural designs |
| Maintenance | Rust protection may be needed | Requires coating (galvanized, PVC, stainless steel) | Material-dependent (aluminum/stainless are low-maintenance) |
Expanded metal outperforms wire mesh in strength since it’s made from a single sheet without joints or welds.
Wire mesh is lighter but may loosen or deform under pressure.
Sheet metal is the most durable overall, especially in thicker gauges, but doesn’t allow airflow unless modified.
If budget is your top priority, wire mesh is usually the cheapest. Expanded metal offers a balance of cost and strength, while sheet metal can range from affordable (mild steel) to expensive (stainless steel, copper).
Expanded metal is perfect for projects that require durability plus ventilation.
Wire mesh excels in fencing, filtration, and lightweight reinforcement.
Sheet metal wins when you need a solid surface, aesthetic appeal, or complex fabrication.
Always choose the right coating for outdoor use (galvanized, painted, or stainless steel).
Inspect regularly for signs of rust or wear, especially in humid or corrosive environments.
For sheet metal, apply protective finishes to extend life and极 prevent corrosion.
With so many choices available, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed when deciding between expanded metal, wire mesh, and sheet metal. The truth is, there isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. The best choice depends on your project’s budget, environment, and performance requirements.
Let’s break down the most important factors you should consider before making a decision.
Budget
If cost is the biggest concern, wire mesh is usually the most affordable option.
Expanded metal offers a balance of cost and performance, while sheet metal can be either budget-friendly (mild steel) or high-end (极stainless steel, copper).
Strength Requirements
For heavy-duty load-bearing applications, sheet metal is the strongest.
If you need strength with ventilation, expanded metal sheets are ideal.
Wire mesh works well for lightweight reinforcement or fencing but isn’t the best for high-impact needs.
Environment
Outdoor projects exposed to weather should use galvanized or stainless steel to prevent rust.
For marine or highly corrosive environments, aluminum sheet metal or stainless steel wire mesh are reliable choices.
Functionality
Need visibility, drainage, or airflow? Go with expanded metal or wire mesh.
Need a solid surface or something that can be fabricated into a specific shape? Choose sheet metal.
Aesthetics
For architectural facades, decorative panels, or design elements, sheet metal and expanded metal both offer sleek, modern finishes.
Wire mesh tends to be more functional than decorative.
For Fencing and Security:
Choose wire mesh (welded type for strength, woven for flexibility).
For Walkways, Catwalks, and Stair Treads:
Expanded metal sheets provide grip, airflow, and safety.
For Roofing, Automotive, and Industrial Parts:
Sheet metal (steel or aluminum, depending on strength vs. weight needs).
For Decorative Architectural Designs:
Both expanded metal and sheet metal can be customized to create modern, eye-catching finishes.
For Concrete Reinforcement:
Welded wire mesh is the standard choice.
For Marine or Outdoor Projects:
Go with stainless steel sheet metal or aluminum sheet metal for corrosion resistance.

The best metal for construction depends on the project. For structural strength, steel sheet metal is often the go-to option because it can handle heavy loads. If you need reinforcement in concrete, welded wire mesh极 is the standard. For projects requiring both strength and ventilation, an expanded metal sheet works extremely well. Always balance cost, durability, and environmental conditions before making your choice.
Yes, in most cases. Expanded metal is cut and stretched from a single solid sheet, which makes it stronger and more rigid than wire mesh, especially welded types. Wire mesh is great for lighter-duty work like fencing or screening, but if you need heavy-duty flooring or security grilles, expanded metal is the better option.
Not always. Sheet metal is solid and doesn’t allow airflow or drainage, which makes it unsuitable for applications like fencing, filtration, or walkways. However, for roofing, automotive panels, or appliance housings, sheet metal fabrication is the preferred choice because it can be cut, bent, and shaped into precise designs.
Wire mesh applications are incredibly diverse. In construction, it’s used for concrete reinforcement and fencing. In agriculture, it serves as animal cages and crop protection. In industry, it’s common in filtration, sieving, and machine guards. Its flexibility and affordability make it one of the most widely used metal products in the world.
If you want low maintenance, stainless steel sheet metal or aluminum sheet metal are excellent choices because they resist rust and corrosion. Wire mesh and expanded metal sheets can also last long outdoors if they’re galvanized or coated, but they may require periodic inspections to ensure no rust or structural weakening.
The cost of sheet metal fabrication depends on the material and complexity of the project. Simple cuts and bends are affordable, but detailed stamping, laser cutting, or custom shaping can increase costs. Mild steel is budget-friendly, while stainless steel and copper sheets are more expensive due to their durability and appearance.
By now, you should have a clear picture of how expanded metal, wire mesh, and sheet metal compare. Each has its own unique strengths, and the right choice depends entirely on your project’s needs.
If you need lightweight, affordable fencing or concrete reinforcement, go with wire mesh.
If you need durability, ventilation, and slip resistance, an expanded metal sheet is the winner.
If you need a solid, customizable base for fabrication, nothing beats sheet metal.
There’s no universal “best metal for construction.” Instead, it’s about finding the best fit for your specific application. Whether you’re working on industrial flooring, a home improvement project, or architectural design, the right material choice can save you time, money, and maintenance headaches down the road.
In the end, the smartest approach is simple: match the metal’s properties with the demands of your project. That way, you’ll not only get the best performance but also ensure long-term value.
So, next time you’re weighing expanded metal vs. wire mesh vs. sheet metal, you won’t be guessing—you’ll be making an informed decision.
Related content recommendations
Expanded Metal, Wire Mesh, or Sheet Metal: Choosing a Basket Material
Difference Between Expanded Metal, Perforated Metal and Wire Mesh
Expanded Metal Selection Guide for Engineers & Manufacturers
Everything you need to know about pig cage mesh: from galvanized and stainless steel to high-strength 6-gauge wire. Get expert buying tips and advice!
TWhen it comes to wire mesh manufacturers USA, the options are nearly endless. US manufacturers excel at producing a diverse range of wire me
When it comes to selecting stainless steel welded mesh for your project, understanding the difference between 304 and 316 grades is essential.
